Firefox with EULA-screen in next Ubuntu? (Update)
September 15, 2008
The next Ubuntu release will contain (if it does not change) a Firefox which requires you to accept an EULA. According to Mark Shuttleworth this is a requirement from the Mozilla Corporation keep the name Firefox for the next version of Ubuntu.
I think this is a bad idea and I’m not the only one. I would remove Firefox from Ubuntu and take the re-branded version from Debian. I thought when they went with a new name for Firefox, that they are paranoid, but now it looks like they were right!
I think we as community should step up and that these things must be nipped in the bud. If Firefox starts soon every program gets an EULA-screen. After a fresh install of Ubuntu I need to click > 20 EULA screen then.
Update: 5min try for a banner:

Update:
The Mozilla Cooperation has responded with a blog post. But I still say I don’t want a EULA screen even if it shows a FOSS license. Next time we need to accept an EULA when we do a apt-get install blalba.
nf_conntrack and the conntrack program
September 14, 2008
Today I had a problem with my VoIP connection to my provider. The hardware SIP client did not connect for some hours. I had a look at the packets which went over my router into the internet. At the first glance it looked as everything worked right on my side, but the other side did not answer.
15:04:46.131077 IP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.5061 > yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.5060: SIP, length: 532
15:04:47.147701 IP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.5061 > yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.5060: SIP, length: 335
15:04:50.130068 IP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.5061 > yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.5060: SIP, length: 532
15:04:51.147168 IP xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.5061 > yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.5060: SIP, length: 335
But at a closer look i realized that the xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx IP address was not my current IP address, given by the DSL provider, but one from an older ppp session with my provider. It was at once clear that there must be a problem with the connection tracking of IPtables, as the SIP client used an internal IP address and gets masqueraded by the router. If you want to know more about IPtables and connection tracking take a look at this.
Anyway I did at a fast cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack | grep 5060 to get all connection tracking entries for SIP. And I found more than one, here is on example.
ipv4 2 udp 17 172 src=10.xxx.xxx.xxx dst=yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy sport=5061 dport=5060 packets=1535636 bytes=802474523 src=yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy dst=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx sport=5060 dport=5061 packets=284 bytes=114454 [ASSURED] mark=0 secmark=0 use=1
The timeout for this entry is 180 sec and 172 seconds to go, and the SIP client was all the time sending new probes and therefore the connection was never dropped. What can you do in this instance? You can install conntrack. It is a userspace command line program targeted at system administrators. It enables you to view and manage the in-kernel connection tracking state table. If you want to take a look at the manual without installing it (apt-get install conntrack) you can take a look at this webpage which contains the man page. With this program I did delete the entries with the wrong IP address and everything worked again.
I think this program and the knowledge of the connection tracking is important for many of my readers, so I’ve written this post. The current cause to talk about this topic is only one of many, so take a look at it.
Filter the output of command line programs e.g. run by cron
Ever had to run a program by cron which writes always stuff to stdout and you therefore get every time a mail from cron? You did an > /dev/null to get rid of the messages but errors are not written to stderr by this program but also to stdout?
I have sometimes that problem and therefore I’ve written a small python script which is run by cron and launches itself the real program. It takes any output of that program and filters it by configured regular expression rules. Everything that matches a rules is not reported. As soon as one line does not match, this line is reported and followed by the full output of the program to make the error finding easier.
I often let programs run in verbose mode, as it is filtered anyway by the python script and if an error occurs it is nice to have more information at hand. The python script also forwards any provided parameter to the real program.
There is the python script filterOutput.py. Just download it, set the execute permissions and open it in an file editor. following 3 variables are interesting for you:
- programPath: the path to which the script should change before starting the program
- programCommand: the full path of the program to launch and filter
- regexList: the list of regular expressions rules which are used to filter the output of the called programm
UPC (Austrian ISP) started using Sitefinder Service (Update)
September 3, 2008
The Austrian ISP UPC (Chello, Indo, Telesystem) has activated a system which sends your browser to UPC site if a domain could not be resolved. They say that this helps their less tech-savvy customers but I believe it helps them more. Because they can put some ads on this site. They are not the first to try this. 2003 Versign tried something similar (called Sitefinder) but it was stopped by ICCANN and user protests. But that was not a provider.
The system is an Opt-Out one and not Opt-In. You need to perform 5 clicks, fill out a form and time to wait for a support employee to get it deactivated. You should really Opt-Out as the system can lead to problems if an DNS server is responding too slow and the system tells you you’ve a wrong domain name. The other question is what happens with the data gathered by the search engine on this site, which tries to guess what you meant.
Update:
This site (german) contains all info how you can Opt-Out.
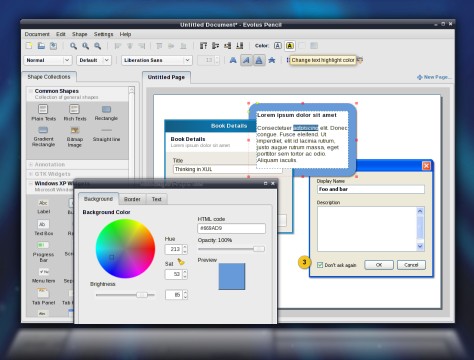
Hidden Firefox feature and the plugin Pencil
I found something interesting, which I guess some already know, but still I though its a nice feature. Copy following into your Firefox browser address bar and hit enter.
javascript:document.designMode='on'; void 0
You can now change a homepage by deleting stuff or replacing some text to test something or making a faked screenshot. I think this can be really handy sometimes and it is build in. Something more sophisticated is following Firefox 3.x plugin, called Pencil (You can also download it here). Pencil is a Firefox add-on to do GUI prototyping and simple sketching, take a look at this blog post which shows what Pencil can do. As a teaser I put a screenshot at the end to this post 😉
Howto install rtorrent and wtorrent within an Ubuntu Hardy VE
August 13, 2008
I didn’t look at rtorrent and wtorrent at first. The first software I found for the web based Bittorrent client I searched was TorrentFlux (to be exact Torrentflux-b4rt). The installing was not complicated, but the software is really bad. For once the php part starts for every torrent a new Bittorrent command line program process which takes really really much memory if you’ve like 10 torrents.Their is also the problem that such processes did tend to hang and it was not possible to solve all problems via the web GUI. The next big part was that the web GUI put a really high CPU load on my browsers if the AJAX update was activated (even if it was set to 30 sec). Basically it was an non integrated set of peaces which made more work than it helped me to save, and as I could not set the overall bandwidth I started to search for something else.
It was not easy to find rtorrrent and wtorrent, don’t know why I didn’t find it when I searched for “web based bittorrent client”. I hope my howto helps somewhat in this regard. The combination of these two applications work for me now without any problems. Low CPU load on the client and Server, small footprint on the server and stable. And it works with torrents which didn’t work with torrentflux.
This Howto describes how to setup rtorrent with the web GUI wtorrent (on lighttpd) on an Ubuntu Hardy and in my case within an OpenVZ VE. Of course this Howto works also if you don’t use visualization and it should also work with the current Debian release. Whats special of my setup is that I want to run the rtorrent and wtorrent within a VE, but the finished data should be stored on an remote NFS server (e.g. a small NAS).
1. OpenVZ VE Setup
First we create the VE from a template, you can download one from OpenVZ:
vzctl create XXX --ostemplate ubuntu-8.04-i386-minimal --hostname torrent
After this we add an IP address and activate the NFS client support within the VE:
vzctl set XXX --ipadd XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX --save
vzctl set XXX --features "nfs:on" --save
After this I recommend to change the limits of your VE, I use following (configured via /etc/openvz/conf/XXX.conf)
KMEMSIZE="11055923:11377049"
LOCKEDPAGES="256:256"
PRIVVMPAGES="525000:572715"
SHMPAGES="21504:21504"
NUMPROC="240:240"
PHYSPAGES="0:2147483647"
VMGUARPAGES="33792:2147483647"
OOMGUARPAGES="26112:2147483647"
NUMTCPSOCK="1440:1440"
NUMFLOCK="1880:2060"
NUMPTY="16:16"
NUMSIGINFO="256:256"
TCPSNDBUF="1720320:2703360"
TCPRCVBUF="1720320:2703360"
OTHERSOCKBUF="1126080:2097152"
DGRAMRCVBUF="262144:262144"
NUMOTHERSOCK="360:360"
DCACHESIZE="3409920:3624960"
NUMFILE="9312:9312"
AVNUMPROC="180:180"
NUMIPTENT="128:128"
Check them on you system that the are not too low. Now you start your VE with
vzctl start XXX
vzctl enter XXX
Take a look at configured DNS servers and that you can reach the Internet with this VE. Put your NFS server into /etc/fstab like this:
yyy.yyy.yyy.yy:/nfsshare /media/nfs nfs soft,udp,auto,user,rsize=32768,wsize=32768 0 0
Don’t forget to create the directory and to apt-get install nfs-common. After this try to mount the share.
2. Configure your firewall
This part of the setup is based on following assumption:
- Your Linux system is used as DSL/Cable Router and
- you’ve only one wordwide IP address and
- your VE has a private IP address.
It is assumed that your VE can connect to the internet, as only the special setup for the bittorrent ports is shown. The following iptables code will redirect the required ports to your VE, where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP of your VE.
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -p tcp --dport 63963:63981 -j DNAT --to-destination xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
iptables -A FORWARD -d xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -p tcp --dport 63963:63981 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -p tcp --dport 63982 -j DNAT --to-destination xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
iptables -A FORWARD -d xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -p tcp --dport 63982 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -p udp --dport 63982 -j DNAT --to-destination xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
iptables -A FORWARD -d xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -p udp --dport 63982 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
3. Install the base and rtorrent
At first the packages we need: (As more packages we can use the less work we’ll have)
apt-get install rtorrent screen mc wget lighttpd gawk php5-cgi php5-common php5-sqlite php5-xmlrpc sqlite unzip php5-curl
Now download following file and save it as /etc/init.d/rtorrent in your VE and activated for automatic startup at boot time with
update-rc.d rtorrent defaults 25
After this we need to add an user under which the rtorrrent process runs and
# adduser --disabled-login rt
# usermod -aG tty rt
# su - rt
$ wget http://robert.penz.name/wp-content/uploads/2008/08/rtorrent.rc -O .rtorrent.rc
$ mkdir /home/rt/session
$ logout
change the /home/rt/.rtorrent.rc file to your needs. You should try out rtrorrent after any config file change, to avoid problems with syntax errors or that stuff.
# su - rt
$ rtorrent
If it started press CTRL-Q to get out.
$ logout
If all worked start it with /etc/init.d/rtorrent start
4. lighttpd setup
This sections shows how to setup lighttpd for rtorrent XML RPC and for wtorrent. Add "mod_scgi" to the server.modules in /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf and add following there too:
url.access-deny = ("~", ".inc", ".db", ".tpl.php", ".cls.php",)
Create following file /etc/lighttpd/conf-available/10-scgi.conf with following content:
scgi.server = (
"/RPC2" => # RT_DIR
( "127.0.0.1" =>
(
"host" => "127.0.0.1", # Ip where rtorrent is listening
"port" => 5000, # Port specified in .rtorrent.rc
"check-local" => "disable"
)
)
)
Enable following two configs by setting a symlink:
# cd /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled/
# ln -s ../conf-available/10-cgi.conf .
# ln -s ../conf-available/10-scgi.conf .
Restart the lighttpd:
/etc/init.d/lighttpd restart
5. Install the wtorrent
Get the newest version and configure it:
# cd /var/www/
# rm index.lighttpd.html
# wget "http://www.wtorrent-project.org/trac/changeset/latest/trunk/?old_path=%2F&format=zip" -O wtorrent.zip
#unzip wtorrent.zip
#mv trunk/wtorrent/* .
#rm -rf trunk
#mkdir tpl_c/
#cd conf
# cp sample.user.conf.php user.conf.php
Change this file according your settings, specially the lines.
define( 'DIR_TORRENTS', 'torrents/');
define( 'DIR_EXEC', '/var/www/');
define( 'DIR_DOWNLOAD', '/home/rt/doing');
After this make everything belong to www-data and read/writable.
#cd /var/www
#chown -R www-data:www-data *
#chmod -R 755 *
Call now
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/install2.php
After the install is finished do following:
# mv install.php install.php_deactivated
# mv install2.php install2.php_deactivated
You should be able to login via http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/
Using the browser history to target online customers of selected banks with malware
August 9, 2008
So the first question is: Howto find out what other sides a visitor of your site visted?
You say that’s not possible with the exception of the referrer in the HTTP header and by placing images/iframes with cookies on some other sites, like google/doubleclick are doing it? Wrong there is an other method which allows you to check the browser history against any list of sites you want to check.
And it is really simple, provide a list with links in a hidden iframe to the browser and a JavaScript. This script checks the style of the links, already visit ones are different than new ones for the browser. For social bookmarking sites you should take a look at following free script, no need to program it by yourself 😉
But maybe you want not only to help your visitors by showing the social bookmarking badge he/she uses, but to get more information on them, e.g. is the visitor a he oder she? You should be able to get that information by the sites the browser has visited, there are ones for likely visited by men and others by women. Check this link out for a test if this site-to-gender formula works for you. (The current version will block your browser for some time).
But now to the more harmful part. You can find out which bank the visitor is using and use this information to do specific attack on the customers of special banks (e.g. the ones for which you’ve a working fake online banking homepage, maybe?). This way an attacker can keep a lower profile as he only tries to attack online banking customers of the banks he wants and not anybody.
Many of such homepages are found by automatic scanning system, but they did not visited the online banking site your want to attack, so you will not show any maleware. This way it is also more unlikely that an attackers site is marked by google as malware infected.
So the question is: Are sites already using this technique to get information about their users?
If you know more about this topic write a comment please!
Ever did some design and wanted blind / dummy text?
August 4, 2008
I found a very nice and easy homepage which generates that kind of text for you. Take a look at Lorem Ipsum. And here is a text generated by it 😉
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Nullam at erat ac sem aliquam tempus. Vivamus nisl odio, euismod quis, tempus quis, porta eu, ipsum. Vivamus est erat, commodo tempus, interdum et, elementum ac, nulla. Vestibulum pede tortor, eleifend at, mattis eget, dignissim eget, lorem. Mauris eu leo. Cras sodales, enim sed faucibus ultricies, tellus tortor blandit nunc, quis lacinia quam est a felis. Ut ac lorem non nunc consectetuer rhoncus. Aenean erat lacus, mollis nec, aliquam et, laoreet quis, neque. Fusce urna lorem, posuere et, molestie eu, facilisis eget, dolor. Integer erat erat, bibendum et, viverra quis, dapibus at, erat. Vestibulum metus. Ut diam erat, sollicitudin sed, ullamcorper at, commodo luctus, eros. Nulla vitae erat. Cras hendrerit commodo mauris.
Aliquam aliquet turpis vitae odio. Etiam luctus orci vitae leo. In et augue eu justo convallis adipiscing. Integer ultricies. Class aptent taciti sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. Nam ante lacus, pellentesque quis, tempor eget, malesuada eget, dui. Proin nec libero. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Sed scelerisque facilisis justo. Suspendisse semper turpis et pede. Pellentesque erat libero, sodales ac, iaculis sed, commodo non, velit. Donec commodo pellentesque elit.
Suspendisse sagittis molestie quam. Cras at dui a magna pharetra ornare. Sed interdum felis quis augue. Maecenas turpis. Suspendisse dui. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Sed vulputate mauris id est. In consectetuer neque nec ipsum. Maecenas consectetuer tellus at pede. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Aenean ante risus, cursus vel, porta ultricies, gravida quis, dolor. Mauris blandit velit ut enim. Pellentesque enim. Praesent vehicula. Maecenas pharetra sollicitudin eros.
DFN CERT warns about Linux root kits
The CERT of the Germany`s National Research and Education Network (DFN – Deutsches Forschungsnetz) warns about attacks on Linux servers, which hide with a root kit. This root kit hides directories and processes from the administrator. The attack is most likely carried out by stolen SSH keys.
Their experts found the directory /etc/khubd.p2/ on the compromised systems but this directory did not show up with ls -l /etc/. But it was possible to change into that directory. As it is very easy to change the source code of the root kid you should check with following:
$ ls -al /tmp/
total 44
drwxrwxrwt 10 root root 4096 2008-08-04 17:58 .
...
tells you the link count and following counts the entries returned by ls:
ls -al /tmp/ | grep "^d" | wc -l
If the do not match, you should really take a closer look. Of course you should use other directories as well. The second way to find leads on this root kit is to send signals to the hidden processes. If a process id is not in /proc, but responding to signals you should also take a closer look:
#!/bin/bash
for PID in `seq 1 65535`; do
if kill -0 ${PID} 2>/dev/null
then
if ls /proc/*/task/*/cmdline | grep "/${PID}/cmdline" >/dev/null
then
true
else
CMD=`cat /proc/${PID}/cmdline`
echo "PID ${PID} versteckt?! cmdline: '${CMD}'"
fi
fi
done
On olders systems the task directory is maybe missing, use /proc/*/cmdline in this case. If you find an active root kit, send a mail to cert at dfn-cert.de.
Damn it! Patch your DNS Server!
July 26, 2008
In the last days an exploit has been released, but still many big companies have not patched their recursive DNS server. According to the Austrian CERT which released a report two third of the recursive DNS are still not patched. These are not small companies or system, according to The Register the big US ISPs like AT&T, BT and Time Warner as Bell Canada are not patched. There are even some hints that attacks are already carried out.
So Damn it! Patch your DNS servers, you’re risking the security of your customers!
Even Microsoft released following security warning Increased Threat for DNS Spoofing Vulnerability which tells you to install the patch MS08-037 at once. But what do you think can be even worse?
Apple
They have still not provided a patch for OS-X-Server, that just shows that apple can’t be taken serious in the server world.
Powered by WordPress
Entries and comments feeds.
Valid XHTML and CSS.
30 queries. 0.068 seconds.





