Howto configure a Mikrotik as central DHCP server with switches as DHCP relays
April 27, 2013
I’ve found many articles about how to configure a Mikrotik RouterOS as DHCP relay or as simple DHCP server, but I didn’t find an article about following setup:
- central Mikrotik DHCP Server (e.g. in the data center)
- multiple VLANs/subnets for clients which are connected via a Layer3 Switch (or even more hops) to the central data center
According to the Mikrotik Wiki and the described options it is possible but there is no example shown and everyone uses the setup wizard to configure a DHCP Server. I’ll get most people don’t know what happens in the background … I’ll show this the old fashioned way. 😉
Setup for this example/howto
For this example we assume that we’ve 4 VLANs with following subnets:
- 10.88.0.0/24 (data center VLAN for the servers and the DHCP server)
- 10.88.10.0/24 (clients network location 1)
- 10.88.11.0/24 (clients network location 2)
- 10.88.12.0/24 (clients network location 3)
The Mikrotik has the IP 10.88.0.100 and connected via ether1 to the data center VLAN. The Layer3 switches use always the .1 IP address in the clients networks.
Layer3 Switches / DHCP Relay
Most (if not all) switches which are able to perform at least simple layer 3 tasks (often also labeled as Layer2+ switches) are able to forward DHCP requests. Check the manual of the switch for this. One setting I came across sometimes leads to problems. It is called “DHCP Relay delay” and is sometimes set to 1 or 2 seconds in the the default configuration. This setting allows a local DHCP Server to answer faster, but sometimes (specially embedded clients) don’t wait that long and run into an error. If there is no local DHCP server set this timer to 0 seconds.
You’ll need to set the DHCP Server IP on the switch to the IP of the Mikrotik.
Mikrotik as DHCP Server
First we configure our pools of the client networks, the mikrotik will give out IPs from this ranges:
/ip pool
add name=poolClientsLocation1 ranges=10.88.10.10-10.88.10.250
add name=poolClientsLocation2 ranges=10.88.11.10-10.88.11.250
add name=poolClientsLocation3 ranges=10.88.12.10-10.88.12.250
Now we need to set the configuration the DHCP Server will handout the clients:
/ip dhcp-server network
add address=10.88.10.0/24 dns-server=10.88.0.100 gateway=10.88.10.1
add address=10.88.11.0/24 dns-server=10.88.0.100 gateway=10.88.11.1
add address=10.88.11.0/24 dns-server=10.88.0.100 gateway=10.88.12.1
And at last we configure which DHCP Relay gets which configuration/pool:
/ip dhcp-server
add address-pool=poolClientsLocation1 authoritative=yes disabled=no interface=ether1 lease-time=1w name=dhcpClientsLocation1 relay=10.88.10.1
add address-pool=poolClientsLocation2 authoritative=yes disabled=no interface=ether1 lease-time=1w name=dhcpClientsLocation2 relay=10.88.11.1
add address-pool=poolClientsLocation3 authoritative=yes disabled=no interface=ether1 lease-time=1w name=dhcpClientsLocation3 relay=10.88.12.1
This is all … 😉
How to get IPv6 with a Mikrotik router via an IPv6 tunnel broker
March 2, 2013
You want to try IPv6 but you’re provider doesn’t give you IPv6 addresses? If your router is a Mikrotik this howto will show you how to use an IPv6 tunnel brocker. This setup will also work for guys with a dynamic IP as most home users do.
Signup with an IPv6 tunnel broker
Go to this Wikipedia page for a list of IPv6 tunnel brokers. I’ve chosen the guys at Hurricane Electric as its free and works also with dynamic IP addresses. Other brokers which provide also 6in4 (in RouterOS called /interface 6to4) which provide a method to update of your IP address via a web URL will work too. If you’ve a static IPv4 address the choosing gets even easier.
Following shows whats needs to be done if you use Hurricane Electric as tunnel broker. The tunnel broker wants to be able to ping your router via IPv4 … lets enable that (only if you disabled ping in the first place)
/ip firewall filter add chain=input icmp-options=8:0 protocol=icmp src-address=66.220.2.74
Move this rule to a place before the blocking rule. This rule is made in a way that it opens the least possible hole which is needed for the tunnel broker to work. Now go to the broker website and do following:
- Click on “Create Regular Tunnel”
- Under “IPv4 Endpoint (Your side):” enter your current IPv4 address
- Choose a server location, for better performance choose one thats not that far away from you. 😉
- After Creating the Tunnel you’ll be shown a web page with following important information you’ll need later:
- Tunnel ID
- Server IPv4 Address
- Server IPv6 Address
- Client IPv4 Address
- Client IPv6 Address
- Routed /64
For the commands I’ll use “Tunnel ID” if you should use your Tunnel Id and so on.
Mikrotik Tunnel Setup
First make sure that you’ve the IPv6 package enabled -use following command:
[admin@mikrotik] > /system package print
Flags: X - disabled
# NAME VERSION SCHEDULED
0 X ipv6 6.0rc11
.....
In this example it is not enabled, so we need to enable it and reboot.
[admin@mikrotik] > /system package enable ipv6
[admin@mikrotik] > /system reboot
Now it should look like this:
[admin@mikrotik] > /system package print
Flags: X - disabled
# NAME VERSION SCHEDULED
0 ipv6 6.0rc11
.....
After this is done we can start configuring. First we need to create the tunnel endpoint on our side.
[admin@mikrotik] /ip firewall filter> /interface 6to4 add comment="Hurricane Electric IPv6 Tunnel Broker" disabled=no local-address="Client IPv4 Address" mtu=1280 name=sit1 remote-address="Server IPv4 Address"
After that we need to tell the router this is his new default gateway.
[admin@mikrotik] /ip firewall filter> /ipv6 route add dst-address=2000::/3 gateway="Server IPv6 Address"
And of course we need also an IPv6 address.
[admin@mikrotik] /ip firewall filter> /ipv6 address add address="Client IPv6 Address"/64 advertise=yes eui-64=no interface=sit1
Now we can test our setup the first time. Lets check if the router is able to ping an IPv6 address in the Internet … we use for this the Google DNS servers.
[admin@mikrotik] > ping 2001:4860:4860::8844
HOST SIZE TTL TIME STATUS
2001:4860:4860::8844 56 58 36ms echo reply
2001:4860:4860::8844 56 58 35ms echo reply
2001:4860:4860::8844 56 58 46ms echo reply
sent=3 received=3 packet-loss=0% min-rtt=35ms avg-rtt=39ms max-rtt=46ms
If this does not work .. try to ping “Server IPv6 Address”. If this does work you got something wrong which the default gateway. If this also does not work .. check your tunnel setup and your IPv6 address.
Mikrotik Setup for the Clients
Now we got it working for the Mikrotik but it would be even better to have IPv6 for the clients. To achieve this we need to configure an IPv6 address on the LAN interface and enable
the advertisement to the clients. Take the “Routed /64” address and add an 1 between the :: and the “/” – this give you the first IP address in the routed subnet.
e.g. 2001:xxx:xxx:xxx::/64 –> 2001:xxx:xxx:xxx::1/64
This leads to following command:
/ipv6 address add interface="your LAN interface" address="IP address in your routed IPv6 subnet" advertise=yes
Now wait a little bit (some minutes) and check if your client operation system got an IPv6 address from the routed subnet. I’ll show it here on an Ubuntu 12.04:
$ ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
inet addr:10.xx.xx.xx Bcast:10.xx.xx.xx Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: 2001:470:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: 2001:470:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx/64 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fe80::xxx:xxx:xxx:xxx/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:5733100 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:4191113 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:4271914251 (4.2 GB) TX bytes:841997928 (841.9 MB)
Interrupt:22 Memory:f6ae0000-f6b00000
You’ll see 3 IPv6 addresses, which are used for following:
- Scope: Link: Only used for communication within the local VLAN … is always there if IPv6 is enabled on the client
- Scope:Global: The second one has the MAC address of this interface in it. This is already a worldwide IP address, but it will tell everyone your MAC address .. which is not that good. So there is the first global one which uses a random part. This feature is called “privacy extension” and the IP is changed by the system after some time. If the privacy extension is activated this IP will be used for communicating.
If you’ve 2 or better 3 IPv6 addresses you can try to ping the Google DNS server:
$ ping6 2001:4860:4860::8844
PING 2001:4860:4860::8844(2001:4860:4860::8844) 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 2001:4860:4860::8844: icmp_seq=1 ttl=57 time=36.7 ms
64 bytes from 2001:4860:4860::8844: icmp_seq=2 ttl=57 time=39.6 ms
64 bytes from 2001:4860:4860::8844: icmp_seq=3 ttl=57 time=48.6 ms
64 bytes from 2001:4860:4860::8844: icmp_seq=4 ttl=57 time=55.3 ms
So this seems to work .. now we need to check if your DNS server reports IPv4 and IPv6 addresses back .. if this is not the case your need to configure your DNS correctly or change to an other server … e.g. the Google DNS Servers.
We’ll verify the correct working with following command:
$ host robert.penz.name
robert.penz.name has address 108.162.198.82
robert.penz.name has address 108.162.199.82
robert.penz.name has IPv6 address 2400:cb00:2048:1::6ca2:c652
robert.penz.name has IPv6 address 2400:cb00:2048:1::6ca2:c752
robert.penz.name mail is handled by 10 mail.penz.name.
This looks good … now you’ll only need to configure a firewall on your Mikrotik as you’re clients now have IPv6 address which can be reached worldwide. Your IPv4 firewall is not enough – you need to filter in /ipv6 firewall.
Mikrotik Setup for users with a dynamic IPv4 address
Now we need to make sure the tunnel broker knows our new IPv4 address after each change. For this Hurricane Electric’s provides a web URL which is described here. Thats nice as there are already some DynDNS update scripts available in the Mikrotik Wiki.
I’ve changed the 5.x one in following parts:
- “username”: Your Hurricane Electric’s username
- “password”: Your Hurricane Electric’s password
- “hostname”: Your “Tunnel ID”
- I’ve changed the
/tool fetchline by replacingmembers.dyndns.orgwithipv4.tunnelbroker.net - And at last I added
/interface 6to4 set 0 local-address=$currentIPafter:log info ("UpdateDynDNS: Dyndns Update Result: ".$result)line as we need also to change our local tunnel IP address.
Thats it .. call this script every few minutes and you’ll have IPv6 connectivity even after your IP address changes. I’ll hope this article gets others also in the IPv6 world.
Retrieve remote FTP or SMTP TLS server certificate
February 26, 2013
With SSL protected resources it is easy to find a command line to retrieve the certificate. Following is documented at many places:
openssl s_client -connect www.google.com:443
But if you use use this with a TLS server, be it SMTP or FTP you’ll get
CONNECTED(00000003)
527654:error:140770FC:SSL routines:SSL23_GET_SERVER_HELLO:unknown protocol:s23_clnt.c:607:
The solution ins quite easy (if you know it) .. use following command line:
openssl s_client -connect ftp.xxxx.at:21 -starttls ftp
or
openssl s_client -connect smtp.xxxx.at:25 -starttls smtp
IPv6 OpenVZ VEs and Debian/Proxmox as host system
February 24, 2013
A friend of mine got a new root server and asked me to help him set it up. And of course I helped and as he got a free IPv6 subnet I thought lets configure it. He is running Proxmox as his host system, which is based on Debian.So this guide is also true for Debian systems which have OpenVZ installed.
- You want to use IPv6 for the host system, you need to add at least following to
/etc/network/interfaces
iface vmbr0 inet6 static
address 2001:xxxx:xxxx:xxx::1
netmask 64
up ip -6 route add default via 2001:xxxxx:beef::1 dev vmbr0
down ip -6 route del default via 2001:xxxxx:beef::1 dev vmbr0Replace
vmbr0witheth0if you’re not using Proxmox and only OpenVZ on Debian. - The ISP my friend has the server located at uses a default gateway, which is not in his IPv6 subnet, you need therefore add a host route. Which is done be following 2 lines
up ip -6 route add 2001:4ba0:fff7:1:beef::1 dev vmbr0
down ip -6 route del 2001:4ba0:fff7:1:beef::1 dev vmbr0 - Restart the networking with:
/etc/init.d/networking restart - Test it with following:
ping6 yourOwnIPping6 defaultGWping6 2001:4860:4860::8888(Google IPv6 DNS Server)
- Add following to
/etc/sysctl.confand make sure it is not defined two times
# IPv6 Packet Forwarding and Proxy NDP
net.ipv6.conf.default.forwarding = 1
net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.proxy_ndp = 1
net.ipv6.conf.all.proxy_ndp = 1 - Call
sysctl -pto activate it at once (so no reboot is required) - Go to
/etc/vz/vz.confand make sure following is in there
IPV6="yes" - You currently can’t add an IPv6 address through the web GUI of Proxmox – so you need to use the CLI (replace with a IP adresse from your IPv6 range
vzctl set <VEID> --ipadd 2001:xxx:xxx::xxx --save - restart the VE, and try the ping stuff from step 4 in the VE. (ps: It can take up to 5 pings before you get a response the first time.)
More is not needed … its quite easy!
ps: don’t forget to add an IPv6 DNS server, if it is a IPv6 only VE. This can currently not be done via Proxmox web GUI.
pps: iptables does not filter IPv6 .. you need ip6tables for this. don’t think that you’re secure, if you didn’t open anything with iptables.
List of IEEE 802.1x hotfixes for Windows 7
February 16, 2013
Most companies which want to enable 802.1x for their wired network run Windows 7 SP1. After activating 802.1x you’ll run into various problems with your Windows 7 boxes. It will work fine in lap tests but it will fail in the real world. Why is that? Because there are many 802.1x bugs in it.
Normally I blog about Linux, networking and security and not Windows related stuff. I’m not an Windows expert but I needed to get it authenticated with my network so needed to look into the matter. I hope it helps other networks guys. I’m working for over 8 month (no not all the time 😉 ) now to get Windows 7 SP1 100% of the time working with 802.1x. Its working 99% of the time, but there are still errors (under rare and special condition) that occur. ;-(
At the time of writing this list I didn’t find any other site that lists the available hotfixes, so I though I start a list. And the description texts from Microsoft to these hotfixes are sometimes brain dead. Anyway some entries are the result of working with the Microsoft Premier Support on cases. If you’ll find any other hotfix, fixit, … please let me know.
ps: We’re using EAP-TLS so I can only write about patches I needed for it.
- KB2481614
If you’re configuring your 802.1x settings via Group Policy you’ll see sometimes EAP-PEAP request from clients in your radius server log during booting even if you’ll set EAP-TLS. This error happened in our case with 1/3 of the boots with some models. The error is caused by a timing problem during startup. Sometimes the 802.1x is faster and sometimes the Group Policy is, and if the 802.1x is faster than the default configuration is taken, which is PEAP. Which lead to a EAP-NAK by the radius server. - KB980295
If an initial 802.1x authentication is passed, but a re-authentication fails, Windows 7 will ignore all later 802.1x requests. This hotfix should also fix a problem with computers waking up from sleep or hibernation – but we’ve disabled these features so I can’t comment on them. - KB976373
This hotfix is called “A computer that is connected to an IEEE 802.1x-authenticated network via another 802.1x enabled device does not connect to the correct network”. I can’t comment on this, as we’ve not deployed 802.1x for our VoIP phones at this point. But it solves one other problem, which is described here. The Windows Vista hotfix for the same problem, linked in the article (There is a third hotfix related but not linked in the article, its for XP – so it seems the problem is through the whole product line), states that if an error occurs Windows is normally hard-coded to ignore EAPOL packets for 20min. I would guess it is the same for Windows 7 too. The linked article tells you to install the patch and set some registry key to lower the value. - KB2769121
A short time ago I found this one: “802.1X authentication fails on a Windows 7-based or Windows 2008 R2-based computer that has multiple certificates”. At time of writing I’m not sure if it helps for something in my setup. According to the symptoms list of the hotfix, it does not, but maybe it helps for something else, as the one before does. - KB2736878
An other error during booting – this time it happens if the read process starts before the network adapter is initialized. Really seems that they wanted to get faster boot times, no matter the costs. - KB2494172
This hotfix fixes a problem if you’ve installed a valid and invalid certificate for 802.1x authentication. The workaround is just deleting the invalid certificate. I’m not sure at this point if it affects also wired authentication. - KB976210
This problem occurs only during automated build processes and if you use an EAP method which needs user interaction – as I don’t do that I can’t comment on this hotfix.
So far this is my list – with the list you should get running Windows 7 and 802.1x nicely, but it is not perfect – Do you know any other patches or workarounds?
Mapping a serial device to a KVM guest may lead to communication problems
December 16, 2012
I’m monitoring my heat pump from my server at home. Last week I moved the monitoring part into a KVM VM and mapped the serial interface (serial to USB adapter) to the virtual machine. Basically it worked, but some queries never worked, but they did before the move and nothing else has been changed. After hours of searching rewriting parts of my software and searching for an error in the heap pump controller, I got the idea to map the serial to USB adapter into the VM and not only the ttyUSB0 device …. and at once it worked again. So this post is basically a hint for others who run into the same problem. I’m talking with following settings to my heatpump 57600, 8, N, 1, and I’m running up to date Centos/SL 6 as host and guest.
ps: Before moving the software into a KVM VM, I had it running withing a openvz container without problems for years, but I needed a custom kernel for it and that doesn’t play that well with a cutting edge BTRFS kernel. 😉
D-root is changing its IPv4 address on the 3rd of January.
December 15, 2012
I repost the full advanced notice from the University of Maryland (which administrates the D root DNS server).
Here the original Post:
This is advance notice that there is a scheduled change to the IPv4 address for one of the authorities listed for the DNS root zone and the .ARPA TLD. The change is to D.ROOT-SERVERS.NET, which is administered by the University of Maryland.
The new IPv4 address for this authority is 199.7.91.13. The current IPv6 address for this authority is 2001:500:2d::d and it will continue to remain unchanged.
This change is anticipated to be implemented in the root zone on 3 January 2013, however the new address is currently operational. It will replace the previous IP address of 128.8.10.90 (also once known as TERP.UMD.EDU).
We encourage operators of DNS infrastructure to update any references to the old IP address, and replace it with the new address. In particular, many DNS resolvers have a DNS root “hints” file. This should be updated with the new IP address.
New hints files will be available at the following URLs once the change has been formally executed:
http://www.internic.net/domain/named.root
http://www.internic.net/domain/named.cache
The old address will continue to work for at least six months after the transition, but will ultimately be retired from service.
A howto for using a Canon PIXMA MG4250 under Ubuntu
December 7, 2012
We’ve bought a new multi functions printer at home, a Canon PIXMA MG4250 and as we’re a Linux shop (PCs and notebooks under Linux, mobiles and tablets under Android) I needed to make the printer work under Ubuntu, in our case Ubuntu 12.04, but the solution should work also under newer versions. We’ve connected the printer via WiFi and therefore need both printing and scanning to work via WiFi.
At least at the time of writing this blog post, searching for a driver or howto was not that easy, specially if you search on the US or European Canon Site …. you need to got the Asian site. You wont find the MG4250 listed there but the MG4270. Take it. I should lead you to a driver site where you can choose “Linux” and than 2 links are interesting for you
- MG4200 series ScanGear MP Ver. 2.00 for Linux (debian …
- MG4200 series IJ Printer Driver Ver. 3.80 for Linux (debian …
I provided direct links to the drivers above but the version may change or the URLs themselves – so maybe the links are broken at the time you’re reading it – in this case you need to click through the site to the new pages.
As you see the drivers are generic for the whole MG4200 series so we’re good. Download the tar.gz files and open a console (e.g. CTRL-ALT-T) and change to that directory.
Printing Part
Lets start with the printing part by extracting the tar.gz and changing into the newly created directory.
$ tar xzf cnijfilter-mg4200series-3.80-1-deb.tar.gz
$ cd cnijfilter-mg4200series-3.80-1-deb/
And let the installation process begin with (if prompted for a password use your user password )
$ ./install.sh
After installing the packages you will be asked some questions. The first one is to connect your printer and switch it on. This is followed by the connection method you’re using (USB vs network). In the case of network it will broadcast within the same subnet, so it only works if the PC and the printer are on the same subnet. After it detected the printer you need knowledge that and choose if it should be the default printer.
After all this just go to the most top right icon and click onto it to the following menu, choose printers …
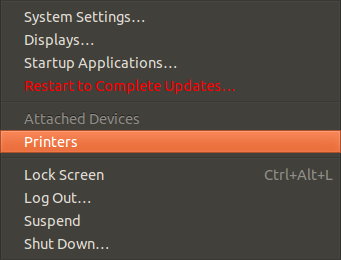
…. and it should show you following with your printer:
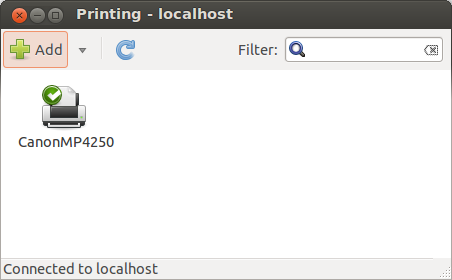
Ok, printing is working … lets go to scanning
Scanning Part
As with the printing part extract the tar.gz and change into the newly created directory.
$ tar xzf scangearmp-mg4200series-2.00-1-deb.tar.gz
$ cd scangearmp-mg4200series-2.00-1-deb/
And again we’re using the install script (if prompted for a password use your user password ).
$ ./install.sh
You’ll be asked no questions and after the installation just start the scanning program with following command
$ scangearmp
It will show you an error message that no configured scanner has been detected, click Ok. Now following window is shown:
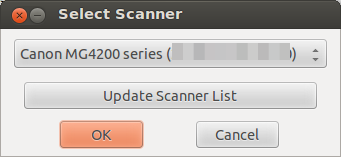
In the case of the first start the list is empty, you need to click onto “Update Scanner List”, after this you should see the same window with your printer. Click onto Ok and you get following:
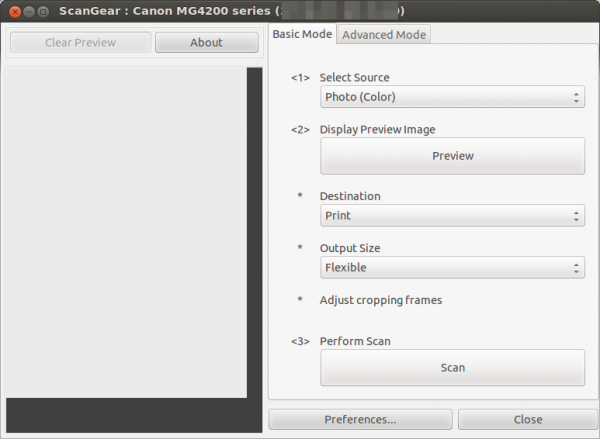
And we’re done.
Update for Ubuntu 13.10 (and possible other versions) users:
If you get following error message:
Unpacking cnijfilter-mg4200series (from .../cnijfilter-mg4200series_3.80-1_amd64.deb) ...
dpkg: dependency problems prevent configuration of cnijfilter-mg4200series:
cnijfilter-mg4200series depends on libtiff4; however:
Package libtiff4 is not installed.
dpkg: error processing cnijfilter-mg4200series (--install):
dependency problems - leaving unconfigured
Errors were encountered while processing:
cnijfilter-mg4200series
Just install the library with
$ sudo apt-get install libtiff4
and the call the install.sh again and it will work.
Howto flush the DNS cache in Ubuntu 12.04?
November 18, 2012
I guess most of you know how to flush the DNS cache on Windows
ipconfig /flushdns
but how to you do it with Ubuntu? Just open with CTR-ALT-T the terminal and type following
sudo /etc/init.d/dns-clean
Howto force scheduled DSL reconnects on Mikrotik routers
November 10, 2012
In my last blog post I have shown how to connect to a PPPoA provider with a Mikrotik router and get the public IP address on the router. I also mentioned that my provider has the bad habit of disconnecting every 8h. As thats not exactly 8h, it tends to wander, but I want at least always the same times. This blog post shows you how to do that if you want the same.
What the script basically does is to force a reconnect at a given time once a day. First we need to make sure that we’ve the correct time on the router. The simplest way to do that is following line:
/system ntp client set enabled=yes mode=unicast primary-ntp=91.189.94.4
But you can only use an IP address there, if you want DNS names take a look hat this script. Also verify that you’ve configured the correct time zone with this command:
/system clock set time-zone-name=Europe/Vienna
Verify the current time with
[admin@MikroTik] > /system clock print
time: 20:56:44
date: nov/04/2012
time-zone-name: Europe/Vienna
gmt-offset: +01:00
dst-active: no
Now we need to write the script, which we to in 2 steps. First we create the script ….
/system script add name=scriptForcedDslReconnect source=""
… than we open it in the editor and add the actual code
[admin@MikroTik] > /system script edit 0
value-name: source
After this you get an editor and just copy and paste following lines:
/interface pptp-client set [find name="pptpDslInternet"] disabled=yes
/interface pptp-client set [find name="pptpDslInternet"] disabled=no
/log info message="pptpDslInternet forced reconnect. Done!"
and press CRTL-O. You can now check if all is correct with (everything should be colored in the script)
/system script print
Now we only need to add it to the scheduler
/system scheduler add name=schedularForcedDslReconnect start-time=00:40:00 interval=24h on-event=scriptForcedDslReconnect
And we’re done, it will disconnect always at 00:40, 8:40, 16:40 … as we wanted.
Powered by WordPress
Entries and comments feeds.
Valid XHTML and CSS.
29 queries. 0.063 seconds.





