Teamspeak 3 Client on Kubuntu 11.10 (oneiric)
November 25, 2011
When you download the TeamSpeak3-Client-linux_*.run (tested with TeamSpeak3-Client-linux_amd64-3.0.2.run) file, extract everything and try to start the TS3 client with ./ts3client_runscript.sh on Kubuntu 11.10 you’ll get following error message:
$ ./ts3client_runscript.sh
Cannot mix incompatible Qt library (version 0x40704) with this library (version 0x40702)
./ts3client_runscript.sh: line 18: 2638 Aborted ./ts3client_linux_amd64 $@
To fix this you need to do following (found the hint here):
- Add following
export QTDIR="."
export KDEDIRS=""
export KDEDIR=""
at line 5 ints3client_runscript.sh - create a file
qt.confwith following content
[Paths]
Plugins = plugins
Hope this works for you too.
Howto copy files from a damaged hard disk with Linux
August 24, 2011
I just got a hard disk which had bad blocks to try to rescue files, but which was too big to use dd_rescue to copy the whole partition on any other hard disk I had, before extracting the files. But in this case the file system directory structure was still readable, so I was able to use following method, which maybe helps someone else.
I mounted the file system read only with following mount -r /dev/sdb1 /mnt and than I created 2 shell scripts.
First File:
#!/bin/bash
cd /mnt/damagedHD/
mkdir /mnt/dirForExtractedFiles/
find . -type d -exec mkdir /mnt/dirForExtractedFiles/{} \;
find . -type f -exec /path2secondscript/rescue_copy.sh {} \;
Second File:
#!/bin/bash
if [ ! -f "/mnt/dirForExtractedFiles/$1" ]
then
dd_rescue "$1" "/mnt/dirForExtractedFiles/$1"
fi
I use 2 scripts as sometimes the hard disk runs into a problem and than stops working until it is powered down and up again. In this case I use CRTL-C to break the loop followed by commenting the first 3 commands in the first file out, and than start it again after the harddisk is mounted again. The “if”-query in the second file makes sure we won’t try files which we already have or the one which lead to the error in the first place.
eAccelerator and the “open_basedir restriction in effect. File() is not within the allowed path(s)” problem
March 6, 2011
This blog post should guard other admins from searching for hours about following error message:
require(): open_basedir restriction in effect. File() is not within the allowed path(s): (/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/:/var/www/xxxxxxxx/include/:/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/tmp/)
in '/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/Translate.php' at the line 81
#0 Piwik_ErrorHandler(2, require(): open_basedir restriction in effect. File() is not within the allowed path(s): (/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/:/var/www/xxxxxxxx/include/:/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/tmp/), /var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/Translate.php, 81, Array ([language] => en,[path] => /var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/lang/en.php)) called at [/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/Translate.php:81]
#1 Piwik_Translate::loadTranslation() called at [/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/Translate.php:81]
#2 Piwik_Translate->loadTranslation(en) called at [/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/Translate.php:35]
#3 Piwik_Translate->loadEnglishTranslation() called at [/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/core/FrontController.php:197]
#4 Piwik_FrontController->init() called at [/var/www/domains/xxxxxxxx/html/index.php:56]
I got it when I tried to install Piwik. I tried everything including setting setting open_basedir to /. It stopped working if I activated the basedir protection and started working if I removed it. After hours searching I found it. I looked into the wrong direction – the problem was not php but eAccelerator. After I found that out it was easy to get to the solution, you need to compile it with the option --without-eaccelerator-use-inode, e.g.this way:
VERSION=0.9.6.1
URL=http://bart.eaccelerator.net/source/$VERSION/eaccelerator-$VERSION.tar.bz2
cd /tmp/
rm -rf eaccelerator-$VERSION
wget $URL
tar xvjf eaccelerator-$VERSION.tar.bz2
cd eaccelerator-$VERSION
phpize
./configure --enable-eaccelerator=shared --without-eaccelerator-use-inode
make
make install
Howto connect multiple networks over the Internet the cheap way
October 17, 2010
I’m quit often asked by 2 types of people how to connect cheaply multiple networks securely over the Internet. The first type are owners of small companies which have more than one office and want to connect them to their central office. And the other type are people who are the de facto IT guy for their family and friends and need an easy way to get into the the other networks.
In the beginning most of them start with with remote connection software like Teamview, VNC, but at some point thats not enough anymore, when the responsibilities grow. The solution that I implement for them is based on the OpenVPN which is a well know, free and secure Open Source VPN solution, which is able to run on cheap hardware. Why do I say it needs hardware when you see on their homepage that it runs on Windows too?
- You want a system with which nobody messes around and so it works for years without ever touching it again. And yes that is possible with the proposed solution. If you can’t reach the router it normally a ISP problem or power outage.
- You don’t have only one Computer in each network and one VPN for each computer is not a good idea if you don’t need it.
- There are also devices in the network where you can’t or won’t install a VPN software. e.g. printer, TV, receiver, acess point, ….
Anyway you can also use this setup to let road warriors into your network over the Internet. I’ll also show how to do that, but it is not the main focus of this blog post.
So about what hardware I’m talking?
- An Accesspoint/DSL/Cable Router which is able to run OpenWRT, or any other system for which OpenVPN is available. I basically stick with systems that can run OpenWRT as I want similar systems to minimize my efforts. To be precise I’m almost always use a Linksys WRT54GL which you get under 40 Euros. But you’re free to use anything else. e.g. a friend of mine has a setup working with a SheevaPlug and Debian on it, an other has a setup running with DD-WRT.
- If you have a local server in the network, be it Linux or Windows based, you can use that do. But don’t use clients if its not for road warriors.
The Setup
You need one OpenVPN node per network/location. In the following example we have
- one central office network with a server and the router is from Internet service provider and we cannot install software on it, the server is also used as DHCP server. (I’ve specially selected that as it shows what additionally needs to be done if the OpenVPN server is not the default gateway for the devices in the network. If for your setup thats in a remote location its the same setup there.)
- one remote office which is connected via cable the Internet. An OpenWRT based router is connected to the cable modem and masquerades the devices behind it.
- one remote office which is connected via DSL to the Internet. An OpenWRT based router inserted after the provider router, both masquerades and to make the life interesting you cannot change anything on the provider router, e.g. add a port forwarding
In this howto we’re working with following subnets:
- 10.23.0.0/24 – central office
- 10.23.1.0/24 – remote office 1
- 10.23.2.0/24 – remote office 2
- 10.23.255.0/24 – transport network remote offices
- 10.23.254.0/24 – transport network road warriors (not in the figure)
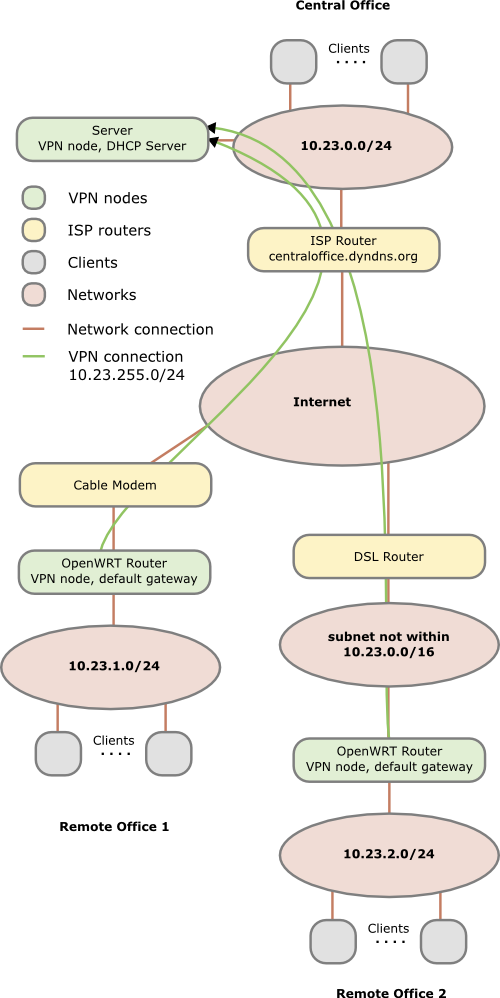
In the figure above you see that each Network has a different subnet – this is important as we need to route packets! Advise: Always use different subnets for different locations you set up. Even if you don’t connect them together at the beginning, make a list which subnets you’ve already used. There are plenty subnets in the 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 range for a single guy or a small company. Use a separate C class networks for each location (e.g. 10.42.0.0/24 for the first, 10.42.1.0/24 for the second and so on).
One subnet is needed as transit network within the VPN to connect the all remote offices to the central one. One subnet is only needed if you also want road warriors to connect to your network.
Preconditions
Common to all locations:
Get OpenVPN installed on all 3 systems. The version can differ a little between the servers which makes it easy if your OpenWRT router has an older version as you use for your main server.
Central office:
- You need to forward 2 UDP ports on the ISP router from the Internet to your server. The example ports I use in this howto are
10000for the VPN connection of the remote offices and10001for the road warriors. - Create an DNS entry for the external IP address of your router. If you’ve a dynamic IP address or no own DNS server/domain you can use for example the dyndns.com service; during this howto I assume centraloffice.dyndns.org as the host name.
- You need to add a routing rule in your DHCP config which tells the clients that
10.23.0.0/16is reachable behind the IP of your sever. And yes the10.23.0.0/16also includes the10.23.0.0/24of the central office, but it is important to remember that the more specific rule counts. The usage of one10.23.0.0/16and not a rule for ech C Class subnet allows you to add remote offices later without changing the DHCP. If your DHCP server is not able to add routing rules, a workaround is possible if your default gateway used by the clients (in this case the ISP router) is able to add the10.23.0.0/16rule to its routing table. In this case every traffic goes first to the default gateway and then back to the server. Thats not nice but for a small network with only a low bandwidth connection to the other networks it is ok. In a big network the security / network guy will cry….. - Make sure that routing is enable on the server. On Linux systems you can check that easily with
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward. If the result is 1 it is enabled otherwise not. - Make sure that if you’ve a local firewall enabled that UDP ports
10000and10001are open.
Remote offices:
All requirements are meet if you’ve installed a modern version of OpenVPN and if the systems have the correct time. This maybe harder than it sounds as most DSL routers don’t have an internal clock that survives reboot. But it is important that the time of the router is bigger than the time the certificates where created, as otherwise the systems will not accept the certificate of the node in the central office. An easy way to make sure that at least this requirement is fulfilled is to set the date at boot to something fixed. I’ll show a simple way to do this later.
Firewall considerations
OpenVPN uses tun* device names for the VPN tunnels. On the central office server you’ve have tun0 for the remote offices and tun1 for the road warrios. For testing purposes you should let any traffice from and to tun0,tun1 and eth0 (LAN interface) through. After you made sure that everything works you should limit that to traffic which is really needed. On the remote offices nodes I recommend to open the traffic permanently in both directions (eth0 to tun0 and tun0 to eth0) as otherwise you need to administer the firewall rules on on multiple systems.
Import: You need also firewalls rules (on the central office server) that allow the traffic from one remote office to the other if you wish that kind of traffic. OpenVPN will be configured in a way that lets that kind of traffic through but without firewall rules that also allow the traffic it will not work.
Setting up a Certicate Authority (CA)
So what is a CA? I copied the first paragraph and linked the explanation of wikipedia as a starting point.
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. The digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others (relying parties) to rely upon signatures or assertions made by the private key that corresponds to the public key that is certified. In this model of trust relationships, a CA is a trusted third party that is trusted by both the subject (owner) of the certificate and the party relying upon the certificate. CAs are characteristic of many public key infrastructure (PKI) schemes.
In more common words each VPN nodes needs to have a one certificate (*.crt – containing the public key and the signature of the CA) and one private key. Each node needs to trust the CA and for this they have the certificate of the CA stored. For each node you need therefore at least 3 cryptography files. The certificate file also contains a flag describing a node as server or client. We’ll configure the OpenVPN clients in a way that will make sure that they connect only to nodes with the server flag.
The CA should be not on one of the VPN nodes but on separate computer. The easiest way to reach a working and secure enough solution for a small company is to put the CA onto a USB stick and only insert it on a secure PC if you’ll need it for generating new certificates.
Now lets get to the doing part, I’ll will assume that you’ve a Linux or Linux like system as your CA system but it will also work on others. In your OpenVPN package you’ll find a directory or .gz file named something like easy-rsa-2.0. On an Ubuntu/Debian system you’ll find it under /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/easy-rsa/2.0/ after installing the package openvpn.
- Copy or extract easy-rsa to a directory of your liking.
- Open the
varsfile in a text editor and scroll down to the end of the file. There you can change the key length to something higher than 1024 but keep in mind that you’ve not the fastest systems if you’re using OpenWRT on a DSL Router. You should also change the default country, city, … entries. The default lifetime of the certificates with 10 years should be enouch 😉 - Type
. varswhich will load the variable in the environment of your current shell. You need to this step every time you start with an fresh shell and want todo any CA operation. - Call
./clean-all– Important: Only do that in the beginning as it will delete your complete CA and certificates if you’ll use it later. - Call
./build-ca mycompany-cato generate the CA, you can leave most questions to the default answers. The important part the common name is already specified a command line parameter. - Call
./build-dhto get a special file for the OpenVPN node in the central office - Call
./build-key-server centralofficenodeto generate the certificate for your central office node. Change the name to something meaningfull. Important: The name (= common name) needs to be unique for all nodes and I recommend to use onlyA-Z,a-z,0-9,-,_as common name. - Call
./build-key remoteofficenodefor each remote location you want to connect. Important: Use a system to choose the names otherwise you’ll loose overview of it if you’ll get more nodes and subnets. e.g. the name of the location/network you typically use to refer to it.
You’ll find all files in the keys subdirectory and you need to copy the .crt, .key of each node and the CA file to the node (and not the files for an other node!) For the node in the central office you need also the dh1024.pem.
road warriors:
If you also want to setup a VPN service for road warriors I recommend to use a separate CA – so make a second copy of the easy-rsa and start again. Import use other names otherwise you will loose the overview.
OpenVPN configuration
Central office:
I assume in this howto that it is a Linux server (Ubuntu/Debian based to be exact) in your central office, but the configuration on for example Windows is the basically the same – just the paths, starting methods and logging stuff are different.
- Create the directory
/etc/openvpn/certs/and copy thecentraloffice.crt,centraloffice.key,ca.crtand thedh1024.pemto this directory and change the permissions for the directory to700and for all files to600and the owner should be root for both. - Create a config file
/etc/openvpn/0_remote_offices.confwith following content:
port 10000
proto udp
dev tun
ca /etc/openvpn/certs/ca.crt
cert /etc/openvpn/certs/centraloffice.crt
key /etc/openvpn/certs/centraloffice.key
dh /etc/openvpn/certs/dh1024.pem
server 10.23.255.0 255.255.255.0
client-to-client
client-config-dir /etc/openvpn/remoteoffice_networks
verb 3
# we can here operate with the same B class network as the more specify rules counts
route 10.32.0.0 255.255.0.0
push "route 10.32.0.0 255.255.0.0"
keepalive 10 120
cipher AES-128-CBC # AES
comp-lzo
max-clients 100
persist-key
persist-tun
- Create the directory
/etc/openvpn/remoteoffice_networksand insert one file for each remote relocation with the name of the common name you choose for it. The files contain only one line with following content for the first remote locationiroute 10.23.1.0 255.255.255.0andiroute 10.23.2.0 255.255.255.0for the second remote location. This tells OpenVPN which remote network is reachable behind which node. - Optional: Copy the road warrior CA stuff needed to the certs directory. Important: Make sure that you use an other name as ca.crt, as you’ve that one for the remote offices.
5. Optional: Create a configuration file/etc/openvpn/1_remote_offices.confwith following content for the road warriors:
port 10001
proto udp
dev tun
ca/etc/openvpn/certs/ca_roadwarrior.crt
cert/etc/openvpn/certs/centraloffice_roadwarrior.crt
key/etc/openvpn/certs/centraloffice_roadwarrior.key
dh/etc/openvpn/certs/centraloffice_dh1024.pem
server 10.23.254.0 255.255.255.0
verb 3
push "route 10.23.0.0 255.255.0.0"
keepalive 10 120
# Maybe you need to comment this out, as your e.g. Windows client uses an slightly other encoding and so you can't transfer data. But if possible AES is the best.
cipher AES-128-CBC # AES
comp-lzo
max-clients 100
persist-key
persist-tun
- Restart the OpenVPN server with
/etc/init.d/openvpn restartand check if the configuration was at least that much correct to start up. - Run
tail -f /var/log/syslog(or your distribution equivalent) to check on entries if the OpenVPN clients try to connect.
Remote Offices:
You need to do following steps for each remote office and replace the filenames with the correct ones for the specify remote location.
- Create the directory
/etc/openvpn/certs/and copy theremoteoffice*.crt,remoteoffice*.keyandca.crtto this directory and change the permissions for the directory to700and for all files to600and the owner should be root for both. - Create a config file
/etc/openvpn/0_to_the_central_office.confwith following content:
client
dev tun
proto udp
remote centraloffice.dyndns.org 10000
resolv-retry infinite
ns-cert-type server
cipher AES-128-CBC
ping 15
ping-restart 45
ping-timer-rem
persist-tun
persist-key
comp-lzo
verb 3
ca /etc/openvpn/certs/ca.crt
cert /etc/openvpn/certs/remoteoffice*.crt
key /etc/openvpn/certs/remoteoffice*.key
- Create an init.d script
/etc/init.d/openvpnwith the permissions755and the content:
# change the date to something bigger than the time you used to generate the certificates
date -s "2010-03-01 10:00:00"
cd /etc/openvpn
openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/0_to_the_central_office.conf --daemon
- Create an symlink to start the init.d script automatically.
cd /etc/rc.d/
ln -s ../init.d/openvpn S65openvpn
- For the first test you should do the steps in the init.d script by hand to check if they work and to see potential errors. For this don’t copy the
--daemonparameter for the OpenVPN as this way you’ve see all errors and can easily stop OpenVPN withCRTL-C. Look also at the OpenVPN log entries on the central office node as it may also contain important error message.
Road Warriors:
The configuration file looks similar to the remote offices ones, just use the 10001 port and use the files from the road warrior CA. On Windows you should use the GUI version of OpenVPN which needs the configuration file normally in c:\programs\openvpn\conf with the extension .ovpn. Copy also the files into the same directory and use no absolute paths as it may varies on different clients and you don’t want to change it for every client.
Conclusion
I hope this howto has shown how easily you can connect various networks via the Internet with Open Source tools and cheap hardware. I’ve you’ve any questions please write them in the comments below that post, I’ll try to answer them. This setup is only the beginning, if there is interest I can show some stuff I use to extend this setup. I’ve also written a blog post some time ago which is interesting for you if you use the same CA for different VPN Server and want to make sure that only a some clients are allowed to connect to a specific server.
Tether a HTC Desire with Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid) via USB
May 21, 2010
You’re as amazed as I’m how short this article is as I’m. I looked through the Internet before I tried it myself and did a look at articles like this. Almost all wrote how complicated that is (e.g. a HTC Software for Windows that works or not) or that you need a software like PDAnet. Thats absolutely not true for the HTC Desire with an Ubuntu 10.04 notebook/netbook. I just connected both via the shipped USB cable and selected on the Desire to share the Internet connection. And guess what happend the Network Manager told me that I’m connected to the network. I couldn’t believe it so I flipped to my shell windows and did a ping. And yes, I was connected. I really don’t understand the problem now the people have. Wrong OS on the notebook? 😉
Some guys in the Linux/Open Source world talked with each other and made it just works out of the box – no special applications or drivers – it just worked. Big THX guys!!! I really love my Ubuntu and Android!
Automating VMware modules reinstall after Linux kernel upgrades
May 15, 2010
I found a nice blog post for you guys that run Linux systems within Vmware be it Server or ESX. After each kernel update from your distribution you need to manually recompile/reconfigure your Vmware kernel modules. What makes that even worse is that during that time you don’t have a network connection, so no ssh script magic if you’ve more than one Linux in a Vmware. But there is a solution for this problem, just take a look at this blog post.
Howto install TeamSpeak 3 server on Ubuntu 10.04 (Lucid)
It has been a long time since my last post – I’m sorry for that but I didn’t have the time. Anyway I just installed TeamSpeak 3 on a Ubuntu 10.04 for a friend and want to share that info. Getting TeamSpeak running is mostly not the problem but you don’t want to start it after every boot by hand or run it as root. This Howto shows what I did. I assume that all user actions shown in this howto are performed as root or after executing sudo bash.
First you need to create a user under which the TeamSpeak server should run by executing following command:
adduser --disabled-login teamspeak
Now we need to get the software (64bit in my case)
wget http://ftp.4players.de/pub/hosted/ts3/releases/beta-22/teamspeak3-server_linux-amd64-3.0.0-beta22.tar.gz (Take also a look if a new version is out when you install your server)
and extract it
tar xzf teamspeak3-server_linux-amd64-3.0.0-beta22.tar.gz
We move it to a nice place with
mv teamspeak3-server_linux-amd64 /opt/ts3
and give it to the user teamspeak
chown -R teamspeak /opt/ts3
If you take a look into the /opt/ts3 directory you’ll see that there is a already a start/stop script (ts3server_startscript.sh), we will utilize it. Create a init.d file with pasting the content after executing cat > /etc/init.d/teamspeak :
#! /bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: teamspeak
# Required-Start: networking
# Required-Stop:
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: S 0 1 6
# Short-Description: TeamSpeak Server Daemon
# Description: Starts/Stops/Restarts the TeamSpeak Server Daemon
### END INIT INFO
set -e
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
DESC="TeamSpeak Server"
NAME=teamspeak
USER=teamspeak
DIR=/opt/ts3
DAEMON=$DIR/ts3server_startscript.sh
#PIDFILE=/var/run/$NAME.pid
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/$NAME
# Gracefully exit if the package has been removed.
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
cd $DIR
sudo -u teamspeak ./ts3server_startscript.sh $1
Now press ENTER and CTRL-D and you’ve inserted the content into the file. Set the permission correctly with
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/teamspeak
and now you can try it out by calling
/etc/init.d/teamspeak start
Take note of the login and token as you will need them later. You can also look for them in the log files in /opt/ts3/logs/. The last thing you need to do now is to make sure the init script is executed at boot time by using following command:
update-rc.d teamspeak defaults
At last if you’ve a firewall running on your system you need to make sure that you open all your ports. To find out which ports are used by teamspeak use following command:
# netstat -lnp | grep ts3
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10011 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 30232/ts3server_lin
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:30033 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 30232/ts3server_lin
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9987 0.0.0.0:* 30232/ts3server_lin
I hope this howto helped someone and write a comment if you found an error or a better way to do something. Now you just need to point your TeamSpeak client to the server and go to the menu entry “permissions | use token” and copy and past the token from above into the edit box. (only insert the chars behind “token=”)
Workaround for routing WOL (Wake on LAN) packets with Linux
January 16, 2010
If you want to send a WOL packet to a PC within your subnet it is really easy. Just install a program like wakeonlan (apt-get install wakeonlan) and type something like:
wakeonlan 01:02:03:04:05:06
But how to you send a WOL packet to an other subnet? Basically you use a UDP packet and send it to the broadcast address of the other network. e.g. with wakeonlan it looks like this
wakeonlan -i 192.168.1.255 01:02:03:04:05:06
But you need support for this from your router, as normally they don’t allow sending to the broadcast address from other networks. Professional routers/layer3 switches have support for this (you just need to enable it), but you’ve a Linux router at home? (e.g. one with Openwrt or Debian/Ubuntu)
The simplest way to get it working is to enter following on the router (rerun it at every boot):
arp -s 192.168.1.254 FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
This tells the router that the given IP has a MAC address which is used for broadcasts. Now you only need to send the packet to this new “broadcast” address instead of the real one. So your wakeup call looks like this:
wakeonlan -i 192.168.1.254 01:02:03:04:05:06
ps: you should only enable something like this on a trusted network and the IP address you use should be not used by any other device.
KDE 4.x and Autostart
September 3, 2009
I was told by some fellow Linux guys that with KDE 4.x there is no Autostart possible anymore. I just wanted to write this blog post to show them that it is still possible even if it not in the KDE menu. Just create following directory if it does not exists
mkdir ~/.kde/Autostart
Some distributions may use .kde4 instead of .kde. Now just place a symlink into this directory with a command like this one for dropbox.
ln -s ~/.dropbox-dist/dropbox ~/.kde/Autostart/dropbox
At least on my Kubuntu systems with KDE 4.3.x that works. 😉
Mini-Howto: Restore Windows MBR/Bootloader with Linux
August 26, 2009
I’m often, at least more than I care, asked how to restore a Windows MBR/bootloader without having a windows install cd or a dos boot disk at hand. It’s quite easy you need just a Linux live cd like (the Ubuntu live cd or Knoppix) or an installed Linux you want get rid of. I really don’t know why you want to do the second, but anyway here are the 2 solutions I know of.
Boot Linux and make sure you’ve a working Internet connection and type following on the terminal/konsole.
1. Solution
sudo apt-get install syslinux
if the package got installed use following to write the MBR.
sudo dd if=/usr/lib/syslinux/mbr.bin of=/dev/sda
2. Solution
sudo apt-get install mbr
if the package got installed use following to write the MBR.
sudo install-mbr -i n -p D -t 0 /dev/sda
Common for both
Replace sda if you want to install the MBR to a different drive. Take a look at your hard disks with sudo fdisk -l if you’re unsure. Finally reboot and your windows should boot.
On request I put this comment from a guy (whats to be anonymous) up to the main article.
Dear Robert,
You have given an excellent article. And I know how much useful it may be to a frustrated person trying to get their work done.
But I sincerely request you to do one last job of giving them a last revealing information about alleged non friendliness of linux derivatives. I think at the moment when people are visiting your post they are frustrated and they vent their ire on linux without getting the other side of the story.
Please consider my suggestions below:
In response to your post, people have been wrongly complaining (in the comments) about the user unfriendliness of ubuntu and other linux variants etc in favour of Microsoft Windows. They think that after installing a linux variant they are unable to install the Microsoft’s Windows back, even after deleting all the partitions.
This actually happens because as soon as a Microsoft Windows OS installer sees a non Microsoft bootloader (for example, GRUB), it refuses to install and says something like the environment is incorrect. Sadly further, it does not explain the ‘environment’ (which could allow a user may look up a solution). And neither does it provide there, a straightforward option to overwrite the other bootloader with its own (even if you delete all the partitions on the disk from the Windows Installer or from the outside!).
I think the Windows implementers chose not to overwrite a foreign boot loader because they did not want to support a non Microsoft OS alongside their own. But the unfortunate thing is they should not do this when not even a single partition is allocated (then obviously there can be no OS installed).
Please let the readers know that it is the Microsoft windows which does not support any non Microsoft OS sitting along side itself and not necessarily the other way round. Please put this information in the main post itself, since otherwise it gets buried under the volume of the comments.
Powered by WordPress
Entries and comments feeds.
Valid XHTML and CSS.
34 queries. 0.077 seconds.





